Note
Go to the end to download the full example code.
Compute Accuracy, Precision, Recall, and F1 on the Wine dataset¶
We’ll use Scikit Learn to compute these metrics for us.
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
from torch.utils.data import DataLoader
from sklearn.metrics import (
accuracy_score, precision_score, recall_score, f1_score, confusion_matrix
)
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
# for number-crunching
import numpy as np
# for dataset management
import polars as pl
# for data visualization
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import seaborn as sns
Load the Wine dataset¶
We’ll use the Wine dataset from the UCI Machine Learning Repository. We’ll create a new variable, “good_quality”. If the wine quality is greater than 5, we’ll set “good_quality” to 1 (True), otherwise we’ll set it to 0 (False).
url = "https://archive.ics.uci.edu/ml/machine-learning-databases/wine-quality/winequality-red.csv"
df = pl.read_csv(url, separator=";", infer_schema_length=int(1e5))
df = df.rename(lambda col_name : col_name.replace(" ", "_"))
# Drop a few outliers
df = df.filter(df["total_sulfur_dioxide"] < 200)
z_scores = [
(pl.col(col) - pl.col(col).mean()) / pl.col(col).std()
for col in df.columns
if col != "quality"
]
df = df.select([
pl.col("quality"),
*z_scores
])
# create a new column for binarized (boolean) quality
df = df.with_columns(
pl.when(df["quality"] > 5).then(1).otherwise(0).alias("good_quality")
)
df
Convert to torch tensors¶
Note that we pass all columns except “quality” and “good_quality” to the input tensor. The target tensor is the “good_quality” boolean variable column.
train_tensor = df.select(
[col for col in df.columns if col not in ["quality", "good_quality"]]
).to_torch().float()
labels_tensor = df.select("good_quality").to_torch().float()
print(f"train_tensor shape: {train_tensor.shape}", f"labels_tensor shape: {labels_tensor.shape}")
train_tensor shape: torch.Size([1597, 11]) labels_tensor shape: torch.Size([1597, 1])
Split the data¶
train_data, test_data, train_labels, test_labels = train_test_split(train_tensor, labels_tensor, test_size=.1)
# then convert them into PyTorch Datasets (note: already converted to tensors)
train_dataset = torch.utils.data.TensorDataset(train_data, train_labels)
test_dataset = torch.utils.data.TensorDataset(test_data, test_labels)
# Finally, create the DataLoader objects
n_samples = test_dataset.tensors[0].shape[0]
train_loader = DataLoader(dataset=train_dataset, batch_size=32, shuffle=True, drop_last=True)
test_loader = DataLoader(dataset=test_dataset, batch_size=n_samples, shuffle=False)
Define the model¶
Note that we have 11 input features and 1 output feature (the target), which
match the number of columns in train_tensor and labels_tensor, respectively.
class WineNet(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
### input layer
self.input = nn.Linear(11, 16)
### hidden layers
self.fc1 = nn.Linear(16, 32)
self.fc2 = nn.Linear(32, 32)
### output layer
self.output = nn.Linear(32, 1)
# forward pass
def forward(self, x):
x = F.relu( self.input(x) )
x = F.relu( self.fc1(x) )
x = F.relu( self.fc2(x) )
return self.output(x)
Train the model¶
We want to train the model to predict whether a wine is of good quality or not, based on the wine characteristics.
wine_net = WineNet()
num_epochs = 500
# loss function and optimizer
lossfun = nn.BCEWithLogitsLoss()
optimizer = torch.optim.SGD(wine_net.parameters(), lr=.01)
# initialize losses
losses = torch.zeros(num_epochs)
train_accuracies = []
test_accuracies = []
# loop over epochs
for epochi in range(num_epochs):
# loop over training data batches
batch_accuracies = []
batch_losses = []
for x, y in train_loader:
# forward pass and loss
y_hat = wine_net(x)
loss = lossfun(y_hat , y)
# backprop
optimizer.zero_grad()
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
# loss from this batch
batch_losses.append(loss.item())
# compute training accuracy for this batch
accuracy = 100 * torch.mean(((y_hat > 0) == y).float()).item()
batch_accuracies.append(accuracy)
# end of batch loop...
# now that we've trained through the batches, get their average training accuracy
train_accuracies.append( np.mean(batch_accuracies) )
# and get average losses across the batches
losses[epochi] = np.mean(batch_losses)
# test accuracy
x, y = next(iter(test_loader)) # extract X, y from test dataloader
with torch.no_grad(): # deactivates autograd
y_hat = wine_net(x)
test_acc = 100 * torch.mean(((y_hat > 0) == y).float()).item()
test_accuracies.append(test_acc)
Compute the accuracy, precision, recall, and F1 score on the train and test sets¶
train_predictions = wine_net(train_loader.dataset.tensors[0])
test_predictions = wine_net(test_loader.dataset.tensors[0])
# initialize a dictionary to store the metrics
train_metrics = [0, 0, 0, 0]
test_metrics = [0, 0, 0, 0]
# compute the metrics on the train set
true_labels = train_loader.dataset.tensors[1]
train_predictions = train_predictions > 0
train_metrics[0] = accuracy_score(true_labels, train_predictions)
train_metrics[1] = precision_score(true_labels, train_predictions)
train_metrics[2] = recall_score(true_labels, train_predictions)
train_metrics[3] = f1_score(true_labels, train_predictions)
# compute the metrics on the test set
true_labels = test_loader.dataset.tensors[1]
test_predictions = test_predictions > 0
test_metrics[0] = accuracy_score(true_labels, test_predictions)
test_metrics[1] = precision_score(true_labels, test_predictions)
test_metrics[2] = recall_score(true_labels, test_predictions)
test_metrics[3] = f1_score(true_labels, test_predictions)
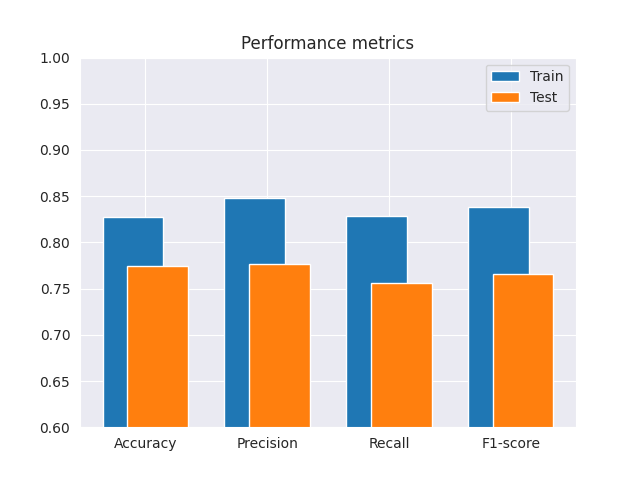
for i, metric in enumerate(['Accuracy', 'Precision', 'Recall', 'F1-score']):
print(f'{metric} (train): {train_metrics[i]:.2f}')
print(f'{metric} (test): {test_metrics[i]:.2f}')
Accuracy (train): 0.83
Accuracy (test): 0.78
Precision (train): 0.85
Precision (test): 0.78
Recall (train): 0.83
Recall (test): 0.76
F1-score (train): 0.84
F1-score (test): 0.77
Plot the metrics¶
sns.set_style("darkgrid")
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
ax.bar(np.arange(4) -.1, train_metrics, .5)
ax.bar(np.arange(4) +.1, test_metrics, .5)
ax.set_xticks([0, 1, 2, 3], ['Accuracy', 'Precision', 'Recall', 'F1-score'])
ax.set_ylim([.6,1])
ax.legend(['Train', 'Test'])
ax.set_title('Performance metrics')
plt.show()
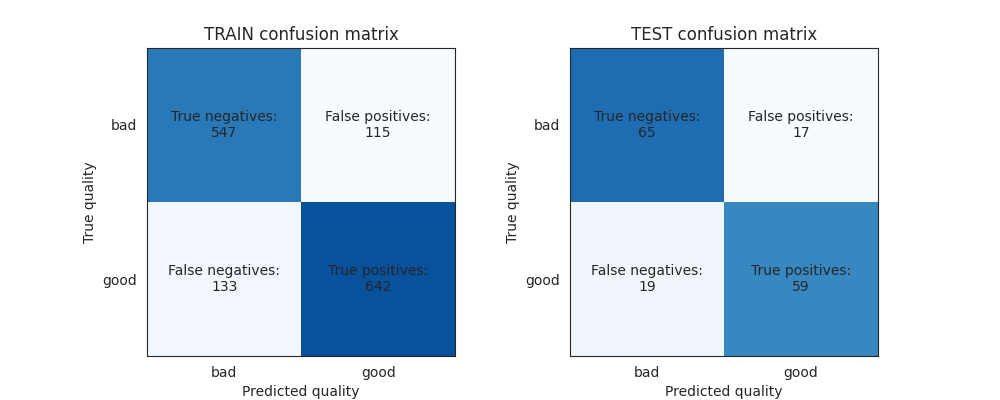
Show the confusion matrices¶
Confusion matrices
true_labels_train = train_loader.dataset.tensors[1]
true_labels_test = test_loader.dataset.tensors[1]
train_conf = confusion_matrix(true_labels_train, train_predictions>0)
test_conf = confusion_matrix(true_labels_test, test_predictions>0)
sns.set_style('white')
fig, axes = plt.subplots(1, 2, figsize=(10,4))
# Confusion Matrix (train)
axes[0].imshow(train_conf, 'Blues', vmax=len(train_predictions)/2)
axes[0].set_xticks([0,1])
axes[0].set_yticks([0,1])
axes[0].set_xticklabels(['bad','good'])
axes[0].set_yticklabels(['bad','good'])
axes[0].set_xlabel('Predicted quality')
axes[0].set_ylabel('True quality')
axes[0].set_title('TRAIN confusion matrix')
# add text labels
text_kwargs = dict(ha='center', va='center')
axes[0].text(0, 0, f'True negatives:\n{train_conf[0, 0]}' , **text_kwargs)
axes[0].text(0, 1, f'False negatives:\n{train_conf[1, 0]}', **text_kwargs)
axes[0].text(1, 1, f'True positives:\n{train_conf[1, 1]}' , **text_kwargs)
axes[0].text(1, 0, f'False positives:\n{train_conf[0, 1]}', **text_kwargs)
# Confusion Matrix (test)
axes[1].imshow(test_conf, 'Blues', vmax=len(test_predictions)/2)
axes[1].set_xticks([0,1])
axes[1].set_yticks([0,1])
axes[1].set_xticklabels(['bad','good'])
axes[1].set_yticklabels(['bad','good'])
axes[1].set_xlabel('Predicted quality')
axes[1].set_ylabel('True quality')
axes[1].set_title('TEST confusion matrix')
# add text labels
axes[1].text(0, 0, f'True negatives:\n{test_conf[0,0]}', **text_kwargs)
axes[1].text(0, 1, f'False negatives:\n{test_conf[1,0]}', **text_kwargs)
axes[1].text(1, 1, f'True positives:\n{test_conf[1,1]}' , **text_kwargs)
axes[1].text(1, 0, f'False positives:\n{test_conf[0,1]}', **text_kwargs)
plt.show()
Total running time of the script: (2 minutes 20.310 seconds)